Liao Wen 廖雯
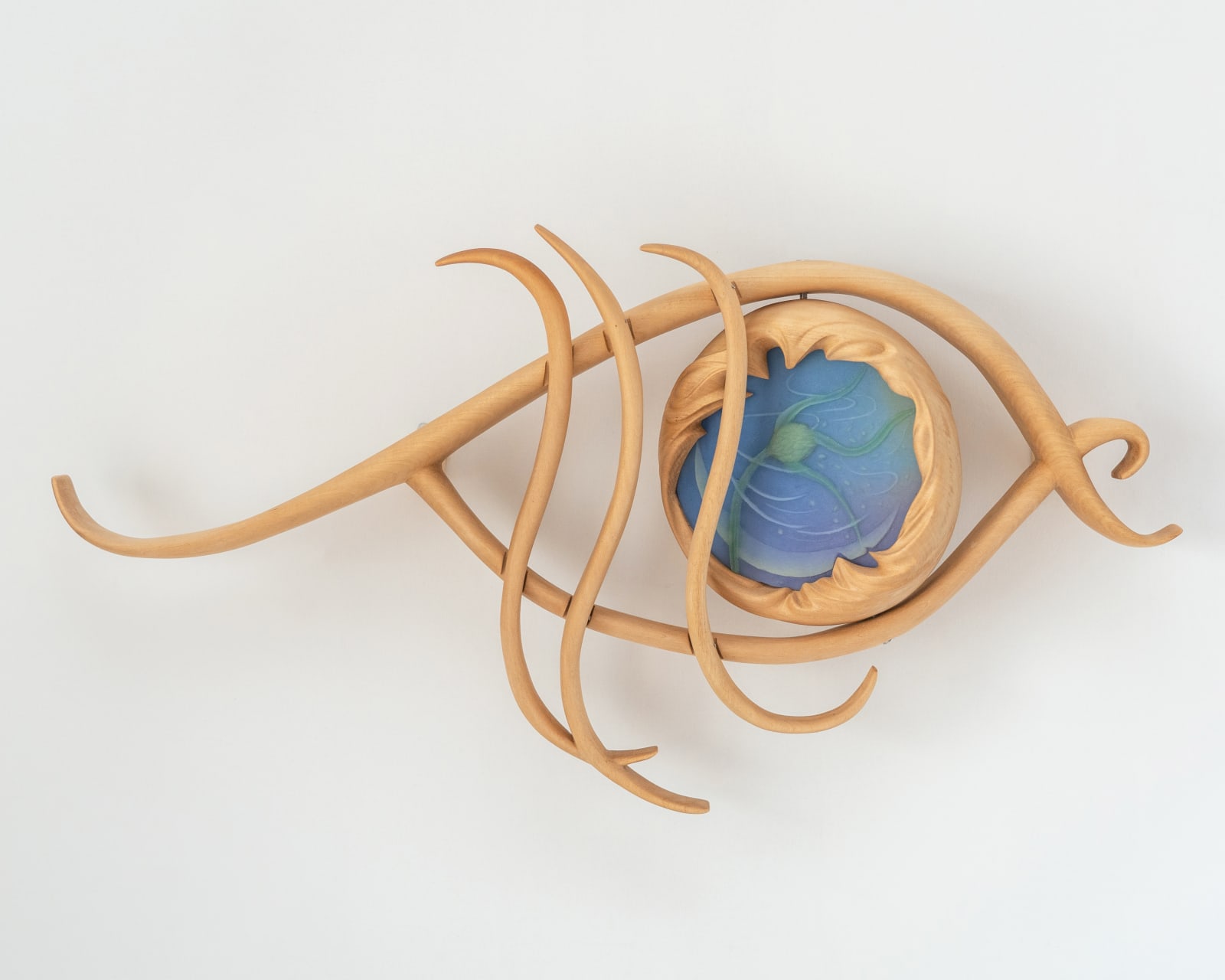
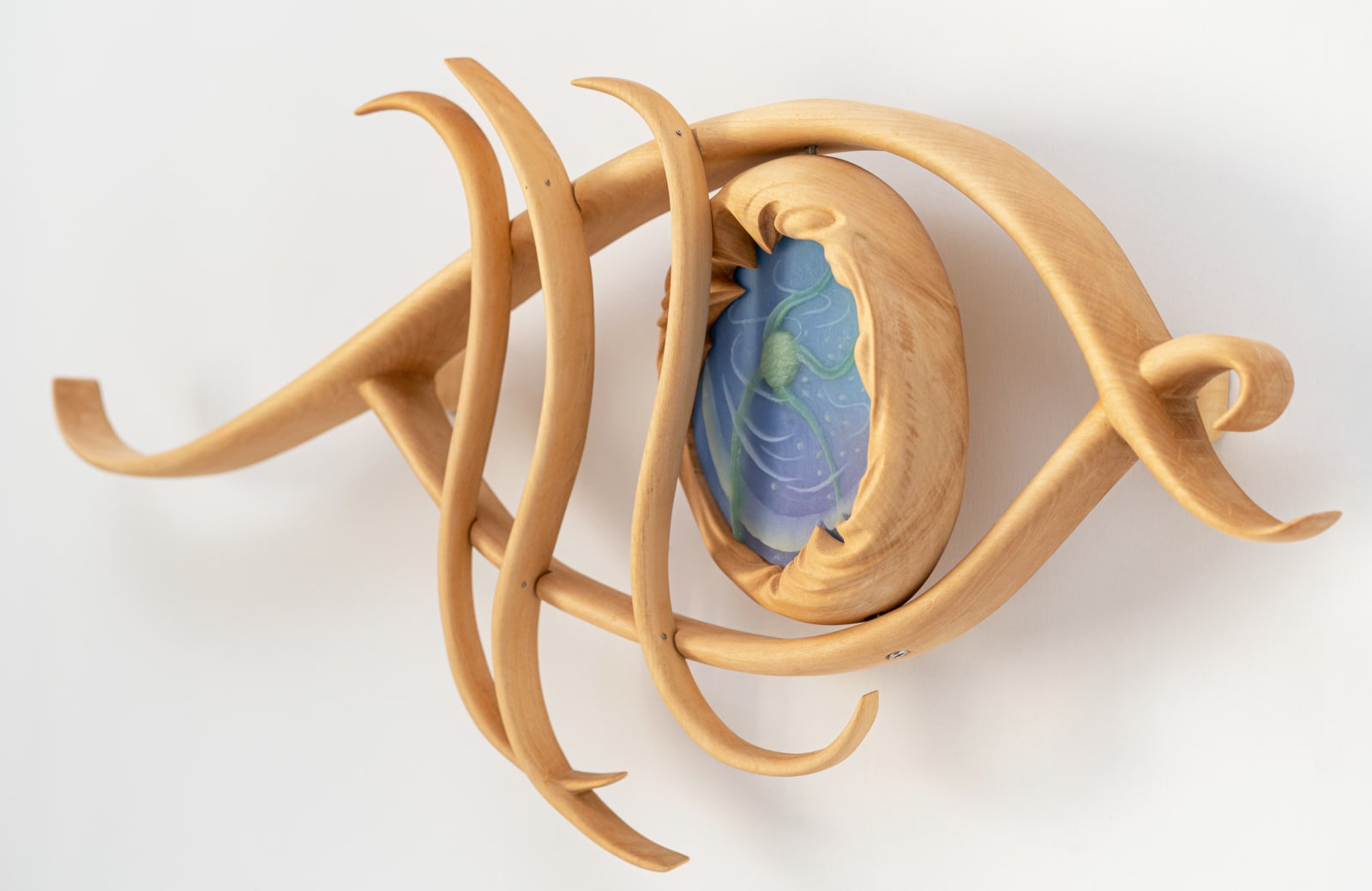
Seeds of the Night Sky 夜空的种子, 2022
silicone, limewood 硅胶、椴木
37 x 67 x 11 cm
14 1/2 x 26 1/2 x 4 1/2 in
14 1/2 x 26 1/2 x 4 1/2 in
更多图片
The work 'Seeds of the Night Sky' is inspired by cyphi, a compound incense that was used in ancient Egypt. The Greek philosopher and historian Plutarch, in his book Moralia,...
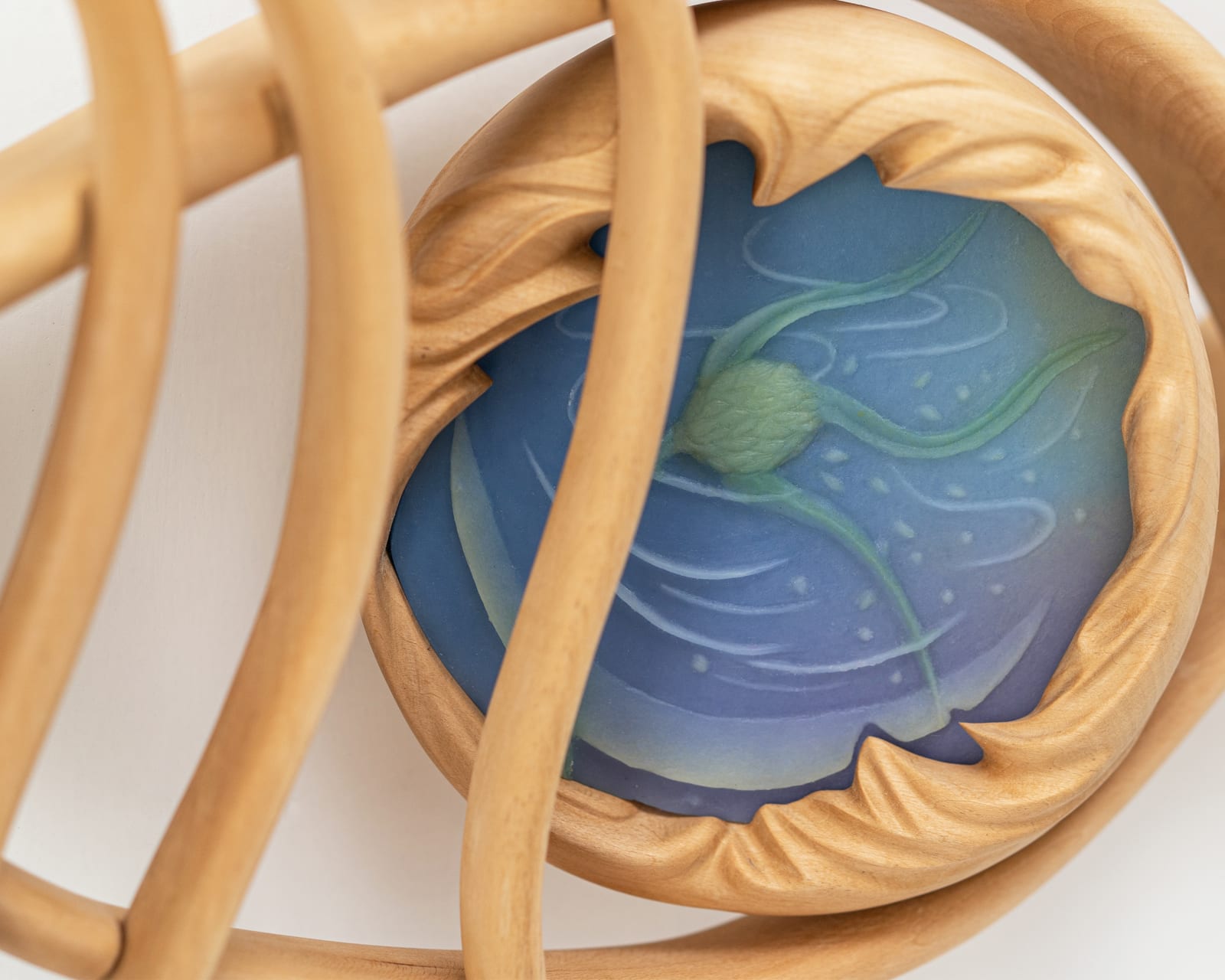
The work 'Seeds of the Night Sky' is inspired by cyphi, a compound incense that was used in ancient Egypt. The Greek philosopher and historian Plutarch, in his book Moralia, describes that “of the ingredients which compose cyphi, there are some which delight more in the night, that is, those which are wont to thrive in cold winds and shadows and dews and dampness… The air at night is a composite mixture made up of many lights and forces, even as though seeds from every star were showered down into one place… The cyphi, since it is compounded of ingredients of all sorts of qualities, they offer at nightfall.” [1] One of the ingredients in cyphi was Acorus calamus, featured in the center of the sculpture. The word ‘acorus’ is derived from the Greek word ‘coreon’, meaning pupil.
The eye reflects moonlight; the seeds are fallen stars.
作品生发于cyphi,它是古埃及的一种神圣香料,常常在夜晚降临时被点燃,献与夜幕。古希腊哲学家和历史学家普鲁塔克在他的著作《道德论集》(Moralia)一书中详述,cyphi的组成物喜爱夜晚,习惯生长于有冷风、阴影、露水的潮湿之处。[1] 菖蒲是cyphi中的一种植物,其属名来自于希腊文的“瞳孔”(coreon)一词 [2],亦是这件作品瞳仁中央的植物原型。
目光映出月色,种子宛若坠落的繁星。
[1] Plutarch., and Frank Cole Babbitt. Moralia. Harvard University Press, 2000. “Isis and Osiris”, p. 189-191.
The eye reflects moonlight; the seeds are fallen stars.
作品生发于cyphi,它是古埃及的一种神圣香料,常常在夜晚降临时被点燃,献与夜幕。古希腊哲学家和历史学家普鲁塔克在他的著作《道德论集》(Moralia)一书中详述,cyphi的组成物喜爱夜晚,习惯生长于有冷风、阴影、露水的潮湿之处。[1] 菖蒲是cyphi中的一种植物,其属名来自于希腊文的“瞳孔”(coreon)一词 [2],亦是这件作品瞳仁中央的植物原型。
目光映出月色,种子宛若坠落的繁星。
[1] Plutarch., and Frank Cole Babbitt. Moralia. Harvard University Press, 2000. “Isis and Osiris”, p. 189-191.